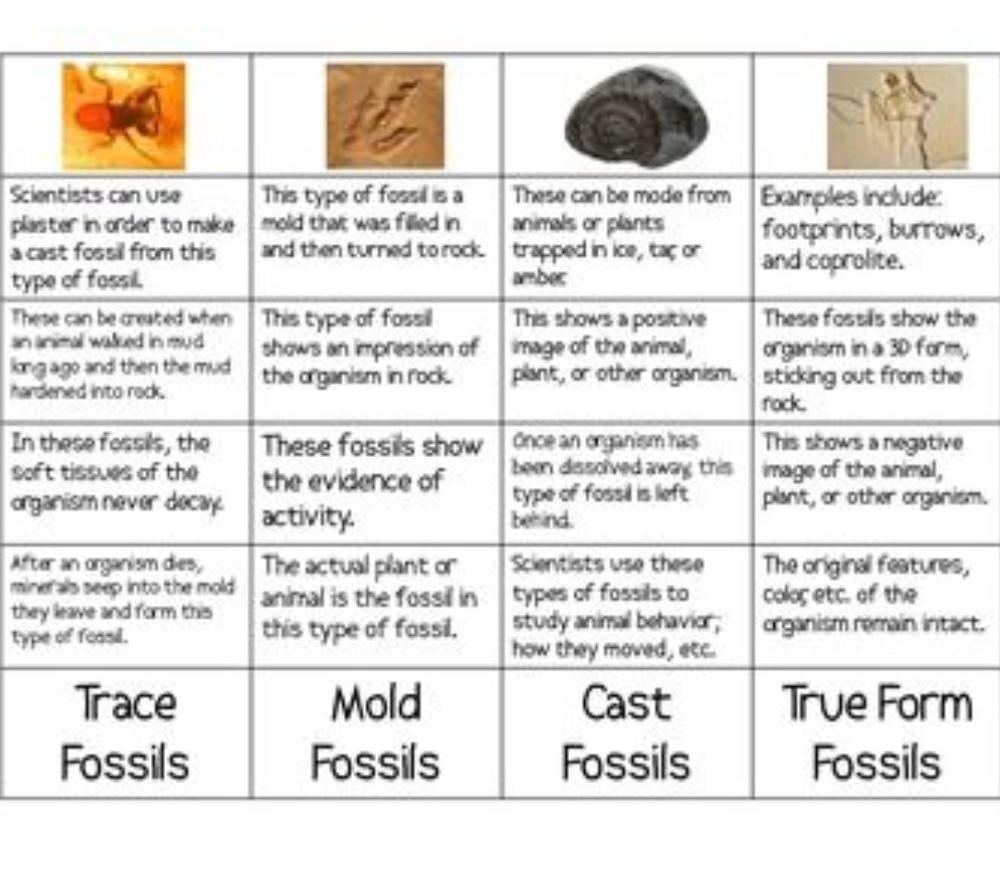
This chart breaks down four main fossil types — Trace, Mold, Cast, and True Form Fossils — using characteristics, formation, and examples:

🐾 Trace Fossils
-
Definition: Evidence of organism activity (not the organism itself).
-
Examples: Footprints, burrows, coprolites (fossilized dung).
-
Key Facts:
-
Show soft tissue movement.
-
Help scientists study behavior, like walking or burrowing.
-
Can be replicated using plaster.
-
🕳️ Mold Fossils
-
Definition: An impression left in rock after the organism decays.
-
Key Facts:
-
Shows shape but not the organism.
-
Often formed in mud that hardens.
-
The actual organism is gone.
-
🪨 Cast Fossils
-
Definition: Created when a mold is filled in, forming a 3D replica.
-
Key Facts:
-
Shows positive space (the organism’s shape).
-
Made from minerals or sediment filling a mold.
-
Helps visualize the full form of the organism.
-
🧊 True Form Fossils
-
Definition: The actual preserved parts of the organism.
-
Examples: Insects in amber, frozen mammoths, bones, shells.
-
Key Facts:
-
Shows the organism itself.
-
Soft tissues may remain intact.
-
Offer the most direct evidence of ancient life.
-
Each type of fossil reveals different insights — from physical form to behavior.